In a scientific research achievement that has attracted global attention, the research team led by Professor Ni Xijun from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, announced that they had re-analyzed an ancient human skull fossil dating back about 1 million years and found a close connection with the mysterious “Denisovans”, according to the latest news. And it reveals a new evolutionary branch of ancient humans in Asia that was previously not fully recognized – “Homo longi”. The relevant research results were published in the international academic journal Science on September 26th, Beijing time, and are regarded as an important milestone in the study of paleoanthropology.
The discovery has pushed forward the timeline of human evolution
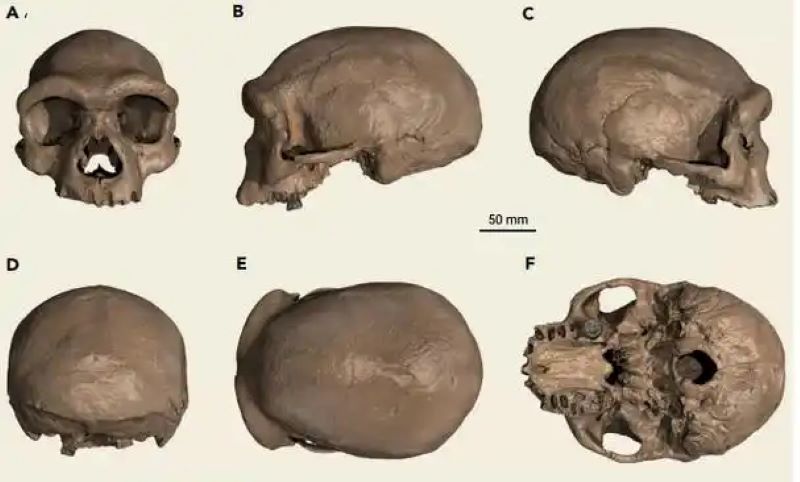
According to the systematic analysis of the research team, this “dragon Man” skull fossil is extremely well-preserved and showcases many unique features of the skull structure. Through advanced chronology, molecular biology, and morphological comparison methods, scientists have clearly classified it into an ancient human branch that is closely related to the Denisovans but exists independently. This discovery has directly advanced the divergence time between modern humans, Neanderthals, and the “Dragon Man” branch by a significant amount, far exceeding the previously widely accepted conclusion in the academic community.
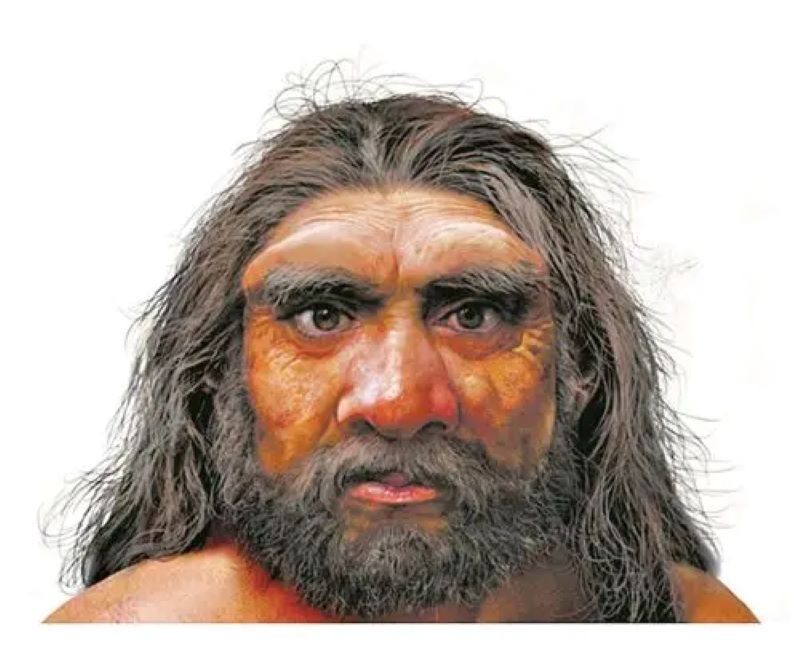
This achievement not only gives us a brand-new understanding of the timeline of human evolution, but also reveals the core position of East Asia in the early evolution of humans. Researcher Ni Xijun said in an interview, “The emergence of the dragon people indicates that our ancestors did not exist in isolation but coexisted, communicated, and even interbred with multiple ancient human groups.”
The “New Puzzle” of paleoanthropology
In recent years, rapid progress has been made in archaeological and paleoanthropological research worldwide. In addition to the early discovered Neanderthals and Denisovans, more and more new species are constantly being named: In 2013, the discovery of Homo Naledi in South Africa caused a sensation; In 2019, Homo luzonensis from the Philippines stepped onto the academic stage. The discovery of Homo giganteus in Northeast China has sparked international heated discussions. Today, the confirmation of “Dragon Man” has further enriched the diversity of the genus Homo and also filled a crucial gap in the history of human evolution.
In a commentary in the same issue of Science, it was pointed out: “This research provides us with a key piece of the puzzle. It not only reshapes our understanding of human evolution but also challenges the long-standing single perspective of ‘Afrocentrism’.” East Asia is very likely one of the important stages for the diverse evolution of human beings.
Academic responses and international attention
This achievement has aroused strong reactions in the international academic community. The British journal Nature commented that the establishment of the “Dragon Man” has provided a brand-new fulcrum for the study of Asian paleoanthropology and may promote the in-depth development of cross-border cooperation projects in the future. John Matthews, an expert in evolutionary biology at Stanford University in the United States, stated: “This research suggests that human evolution is not a straight line but a complex network full of branches and intersections.” China’s discoveries are changing our understanding of the global origin of humanity.
In China, the research results have also attracted widespread public attention. On social media platforms such as Weibo and Zhihu, the term “dragon man” quickly made it to the top of the trending list, with many netizens exclaiming, “The human family tree is getting more and more lively.” Some comments hold that this discovery is not only an academic breakthrough but also reflects that China’s international say in the field of paleoanthropology research is constantly increasing.
Innovation in principles and methods
One of the key reasons for this research breakthrough lies in the innovation of methodology. The research team utilized high-resolution CT scanning and artificial intelligence modeling technology to conduct a three-dimensional reconstruction of the skull fossil, successfully restoring its facial features and cranial cavity morphology. Meanwhile, by combining stable isotope analysis and ancient DNA residue detection, scientists have been able to more precisely locate the evolutionary position of the “Dragon Man”.
Ni Xijun’s team pointed out that although the genomic data of the “Dragon Man” have not been fully obtained yet, its morphological characteristics are highly similar to those of the known Denisovan samples, yet it also shows several independent features, which provide solid evidence for its status as an independent branch.
Future research and challenges
Although the achievements are remarkable, the academic community also warns that this method still faces many challenges. For instance, how can we ensure that the evolutionary status of the “Dragon People” is widely recognized on a global scale? How close is its relationship with modern humans exactly? Is there gene exchange? All these issues require more fossil and molecular evidence to support them.
Furthermore, some scholars have raised concerns: While emphasizing the independence of the “dragon Man”, will it weaken the explanatory power of the existing human evolution model? Anne Schulz, a scholar from the Max Planck Society in Germany, commented: “This research is exciting, but we must be cautious.” The establishment of new species not only requires scientific evidence but also needs to avoid over-interpretation.
A new chapter in the human story
Overall, this research is not only a breakthrough in the academic field but also a deepening of human self-awareness. It reminds us that today’s modern humans are not the only survivors, but have jointly written the long history of evolution with multiple branches of ancient humans.
As the editorial of Science puts it: “Every fossil is a new chapter in the story of humanity.” The appearance of the “Dragon Man” once again proves that our history is more complex and richer than we imagined.
The release of this “latest news” has once again drawn global attention to the study of paleoanthropology in China. As more fossils are unearthed in the future and interdisciplinary research unfolds, the mysteries of human evolution may be gradually solved, and the story of the “dragon Man” is just beginning.













Leave a comment