In a groundbreaking study, Chinese scientists have analyzed lunar samples from the Moon’s far side, revealing that its mantle contains significantly less water than previously thought. This discovery offers new insights into the Moon’s formation and its asymmetric geological features.
Chang’e 6 Mission: Pioneering Lunar Exploration
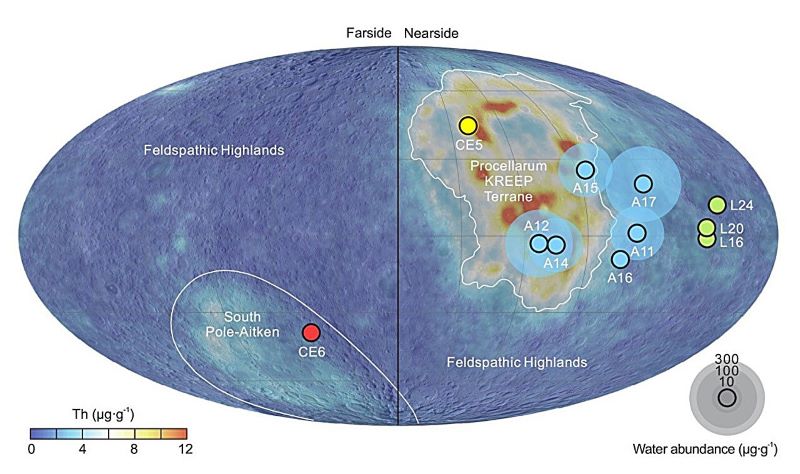
Launched on May 3, 2024, China’s Chang’e 6 mission marked a historic achievement by successfully landing on the Moon’s far side and returning with soil and rock samples. The mission targeted the South Pole–Aitken (SPA) basin, one of the largest and oldest impact craters in the solar system. The return capsule landed in Inner Mongolia on June 25, 2024, bringing back approximately 1,935 grams of lunar material.

Analyzing the Lunar Samples
A research team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted detailed analyses on 578 particles from the returned samples, focusing on mare basalt fragments. Using electron microscopes, they estimated the water content in the mantle source of these basalts to be between 1 to 1.5 micrograms per gram. This is markedly lower than the water content found in samples from the Moon’s near side, which range from 1 to 200 micrograms per gram.
Implications for Lunar Formation Theories
The disparity in water content between the near and far sides of the Moon suggests a hemispheric difference in the Moon’s internal water distribution. This finding aligns with other asymmetrical features observed on the lunar surface and provides critical constraints on the giant-impact hypothesis of the Moon’s origin. According to this theory, a Mars-sized body collided with the early Earth, leading to the formation of the Moon. The lower water content on the far side supports the idea that the Moon’s mantle experienced varying degrees of volatile retention and loss during its formation.
Potential Causes of the Water Content Disparity
Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the lower water content in the Moon’s far side mantle:
- Impact Dynamics: The colossal impact that created the SPA basin may have ejected water-bearing materials toward the near side, depleting the far side of volatiles.
- Magmatic Processes: Variations in volcanic activity and magma ocean crystallization between the two hemispheres could have led to differences in water retention.
- Crustal Thickness: The Moon’s far side has a thicker crust, which may have inhibited the ascent of water-rich magmas, resulting in a drier mantle.
Broader Implications for Lunar Exploration
Understanding the distribution of water within the Moon is crucial for future lunar exploration and potential habitation. Water is a vital resource for life support and can be used to produce fuel for deep-space missions. The discovery of lower water content on the far side suggests that future missions may need to focus on specific regions, such as permanently shadowed craters near the poles, where water ice is believed to exist.
Future Research Directions
While the findings from the Chang’e 6 mission provide valuable insights, scientists emphasize the need for further sampling and analysis to confirm the extent of the water content disparity. Future missions, both crewed and uncrewed, are planned to explore the Moon’s surface and subsurface in greater detail. These missions aim to map the distribution of water and other volatiles, enhancing our understanding of the Moon’s geological history and its potential as a resource for future space exploration.
Conclusion
The analysis of lunar samples from the Chang’e 6 mission has unveiled a significant difference in water content between the Moon’s near and far sides. This discovery not only sheds light on the Moon’s formation and evolution but also informs future exploration strategies. As international interest in lunar exploration grows, such findings underscore the importance of continued scientific investigation to unravel the complexities of our celestial neighbor.












Leave a comment