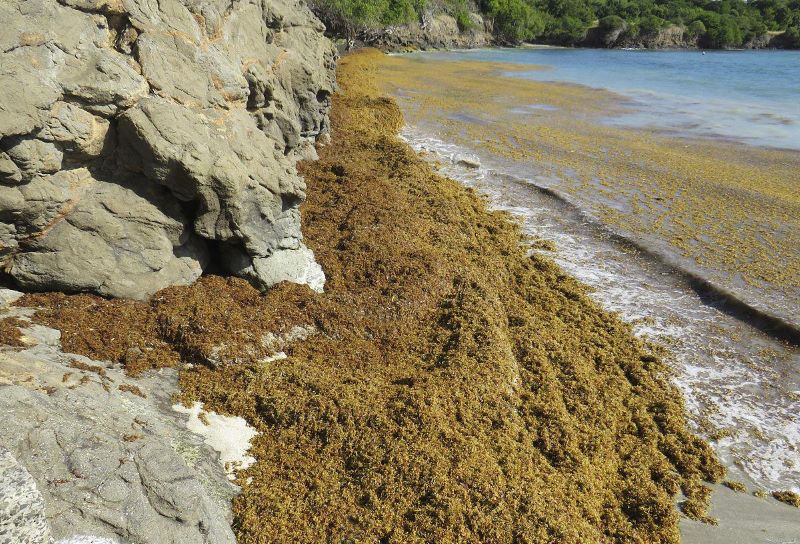
Mexico’s Caribbean coast is a tourist resort, but here at least 600 miles of coastline is suffering from the plague of algae blooms, the sea has begun to turn brown, the beach can also smell the stench emitted by the decomposition of algae. To solve this problem, local scientists have introduced the world’s first automobile powered by biomass gas. The innovative fuel source was invented by the University of the West Indies (UWI) in Barbados, and in addition to using algae as the primary material, the researchers utilized wastewater from a local rum distillery and manure from the island’s native black-bellied sheep. These feces provide important anaerobic bacteria. The research team says that any car can be converted to run on biomass gas with a simple approach that costs about $2,500 in total and takes four hours.
The car is powered by biomass gas produced using algae, a technology that is resourceful and cheap to produce. Algae grows quickly and does not take up valuable arable land, making it an ideal feedstock for biofuels. In addition, scientists are able to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by converting algae into gas that can be used to power automobiles through a clean conversion process. This innovative fuel technology not only provides an environmentally friendly option, but also opens up new avenues to drive the energy transition and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Harm From Algae
In 2011, large swaths of Sargassum washed up on Caribbean beaches, causing considerable distress to local residents. With climate change, more and more sargassum carried by ocean currents is piling up on the beaches, covering the local coastline, and the pungent stench of decaying sargassum is a deterrent for tourists. In 2018, Barbados’ Prime Minister, Mr. Mottley, declared a state of national emergency because of the problem of sargassum.
Algae are not only a threat to tourism. The hydrogen sulfide they release during decomposition also poses a threat to human health, as well as to local wildlife, such as critically endangered sea turtle hatchlings trapped in thick kelp. Sargassum, or seaweed, has been invading Caribbean beaches for more than a decade. Warming oceans and increased marine pollution have fueled the growth of weeds in the Sargasso Sea, which wash up on pristine Caribbean beaches. Once it reaches land, the seaweed begins to rot. Not only are piles of seaweed and the smell of decay unpleasant for tourists, but they also pose a threat to the health of marine animals. Resorts need to spend millions of dollars each year to remove seaweed from their beaches. In recent years, leaders such as Barbados leader Mia Motley and Antigua Prime Minister Gaston Browne have been calling for ecological reparations as the region struggles with rising sea levels and increasingly severe storms. In addition to the Caribbean, Sargassum is also negatively impacting the coasts of West Africa, South America and Florida. The University of the West Indies also hopes to introduce other innovative products based on sargassum, such as pest control products.
The Researchers Initially considered using sugarcane to reduce dependence on expensive imported fossil fuels and help steer the Caribbean toward its ultimate goal of zero emissions. However, although Barbados is one of the few islands that still produces sugarcane, it does not produce enough to meet the team’s ambitious goals, compared to sargassum, which is something that “never runs out”. Moreover, seaweed is an ideal feedstock due to its short growth cycle and wide range of growing environments, which do not require large amounts of fertilizers or water.

Technical Advantages of Biomass Gas Vehicles
In terms of environmental protection: the carbon dioxide produced during the combustion process of biofuel can be absorbed by biomass through photosynthesis during the growth process, thus achieving carbon neutrality. Biofuel is derived from plants, which is a renewable resource with better sustainability than limited petroleum resources. Biomass gas vehicles can reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. The combustion of biofuels produces fewer pollutants, helping to improve air quality and reduce environmental problems such as acid rain and haze.
On the economic side, biomass gas vehicles have a better market prospect as the production process is efficient and less costly. Such vehicles are also able to monitor energy consumption and emissions in real time and make intelligent adjustments to ensure the maximization of fuel utilization. The production of biofuels can promote agricultural development and increase farmers’ income, while contributing to the rational use of land and the improvement of the ecological environment.
Existing Problems of Biomass Gas Vehicles
Despite the technological breakthroughs in biomass gas vehicles, their promotion and application still face some challenges:
- Management: Existing fuel infrastructure needs to be adapted to accommodate biofuels, which involves upgrading and retrofitting gas stations, pipelines, etc. The use of large-scale biofuel crops may have impacts on natural ecosystems, such as biodiversity loss and land degradation. Ensure sustainability of algal fuel production to avoid negative impacts on marine ecology.
- Technical aspects: Biofuels are relatively expensive to produce, especially if the technology is not mature, which limits their large-scale commercial application. Biofuels differ chemically from traditional petroleum fuels and may require adjustments to automobile engines to ensure compatibility and performance.
To overcome these challenges, concerted efforts by governments, enterprises and research institutions are needed to increase R&D investment, optimize production processes, and improve the economics and environmental sustainability of biofuels. Reasonable policies and standards are also needed to guide the healthy development of the biofuel industry. As global concern for environmental impact increases, biomass gas vehicles are expected to become an important choice for low-carbon travel in the future, and the reduction of their production costs and the continuous maturation of their technology will drive the possibility of their large-scale industrialization and application significantly.
The successful implementation of the biomass gas vehicle is the result of a multi-party collaboration involving local universities, research institutes, and government support, demonstrating the importance of science and technology in combating climate change. This event is not only a sign of technological innovation but also an important step in the society-wide transition to renewable energy. Perhaps as the technology continues to mature and market acceptance increases, the seaweed gas vehicle-related industry will gradually grow and develop, and major automakers will also set their sights on this new field, possibly launching more similar models and related products to further promote the popularity of green mobility. For the automobile industry, innovation has become the key to survival, and the development trend of such emerging technologies as algae-powered vehicles happens to provide a new path to explore.