The latest “Electricity Mid-Year Update 2025” released by the International Energy Agency (IEA) pointed out that global electricity demand is growing at an unprecedented rate, and electricity consumption is expected to exceed 29,000 terawatt hours in 2026, reaching a record high. Even more notably, renewable energy power generation will surpass coal for the first time as soon as 2025, becoming the world’s largest source of electricity, marking a historic turning point in the global energy structure.
Demand Growth: Emerging Economies Lead
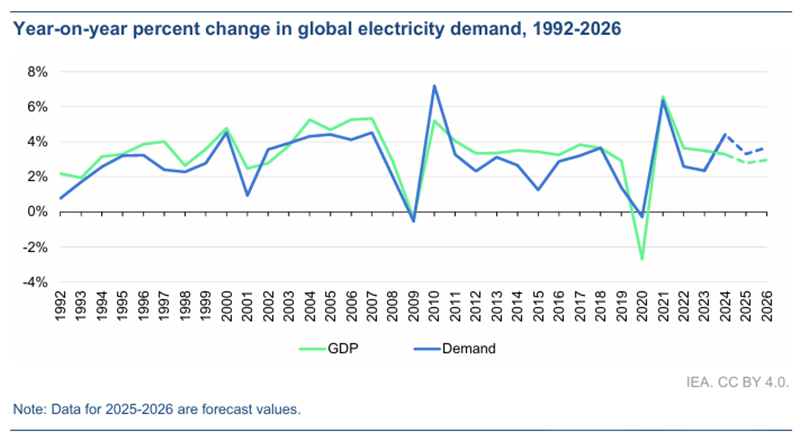
The Electricity Mid-Year Update 2025 shows that global electricity demand is expected to grow by 3.3% in 2025 and 3.7% in 2026, more than twice the growth rate of total energy demand. Emerging Asian economies have become the core growth engines: China’s demand growth rate in 2026 is expected to reach 5.7%, and India’s demand growth rate is expected to reach 6.6%. China’s electricity growth is characterized by “structural optimization”. The service industry has achieved a growth of 7.1% due to electric vehicle charging and data center expansion, and the growth rate of new energy manufacturing industry is particularly impressive. Demand in the United States is expected to grow by 2.3% in 2025, driven by data center expansion.
Supply Change: Renewables Lead
The global electricity supply is undergoing a “historic substitution”. Renewable energy will surpass coal as soon as 2025, when the proportion of coal will drop below 33% for the first time in a century. From 2024 to 2026, the proportion of solar and wind energy will increase from 15% to nearly 20%. Nuclear power production has also reached a new high and is expected to grow by nearly 2% in 2025. Gas-fired power generation has grown steadily, while coal-fired power generation has continued to decline, with the decline expected to expand to 1.3% in 2026.
Regional differentiation: The gap between emissions and electricity prices is widening
Global power generation carbon emissions will enter a “plateau” in 2025 and begin to decline in 2026. China has become the major economy with the largest reduction in emissions due to the large-scale expansion of renewable energy. There are significant regional differences in electricity prices: electricity prices in the European Union and the United States have increased by 30%-40% due to the tightening of natural gas markets; In India and Australia, electricity prices have dropped by 5%-15% due to the expansion of renewable energy. The phenomenon of negative electricity prices in Europe is becoming more and more frequent, exposing the insufficient capacity of the power grid.
Grid Upgrades: Key Challenges for Transformation
The Electricity Mid-Year Update 2025 warns that power grid infrastructure has become a “short board” of energy transition. Large-scale power outages in Chile and Spain in 2025 caused by grid vulnerabilities exposed the system’s insufficient ability to cope with large-scale access to renewable energy. With the acceleration of electrification, the importance of ensuring power supply security has become increasingly prominent. The latest report emphasizes the urgent need to upgrade power grid technology, optimize power reserves, and improve the regulatory system to build a safe and reliable power system.












